Introduction
Starter motor is essentially a powerful electric motor designed to rotate a crankshaft.The starter motor, a humble yet indispensable part, is the silent hero that brings your vehicle to life.It plays a vital role in the operation of your vehicle.Your
automobile, motorcycle, or any other vehicle with an internal combustion engine is effectively powered by its starter motor. It’s the vital energy that surges into action, starting the combustion process in the engine and accelerating your car.
Components of Starter Motor
While the starter motor may seem complex, its basic function is relatively straightforward. It’s essentially a powerful electric motor that is designed to rotate a crankshaft, the rotating shaft that drives the pistons in your engine. Here’s a breakdown of its key components:
- Armature: The rotating part of the motor that generates electricity when it spins.
- Field windings: Coils of wire that create a magnetic field around the armature.
- Commutator: A segmented ring that reverses the direction of current flow in the armature as it rotates.
- Brushes: Carbon blocks that make contact with the commutator, supplying electricity to the armature.
- Bendix drive: A mechanism that engages and disengages the starter motor from the flywheel.
How Starter Motor Works ?
- Ignition: When you turn the ignition key, a circuit is completed, supplying electricity to the starter motor.
- Engagement: The bendix drive engages with the flywheel, connecting the starter motor to the crankshaft.
- Rotation: The armature, energized by the electric current, begins to rotate. This creates a magnetic field that interacts with the field windings, producing a torque that turns the crankshaft.
- Combustion: As the crankshaft turns, the pistons are forced up and down, compressing the air-fuel mixture within the cylinders. The spark plugs then ignite this mixture, causing a combustion reaction that produces power.
- Disengagement: Once the engine starts, the bendix drive disengages, allowing the starter motor to stop.
Battery Cables
While the starter motor is the heart that pumps life into your vehicle, the battery cables are its lifelines. Battery cables are thick, insulated wires that connect the battery terminals to the starter motor and other electrical components in your vehicle. They are
typically made of copper or aluminum, materials known for their high conductivity, ensuring efficient power transfer.
The Importance of Battery Cables
- Power Delivery: Battery cables are responsible for delivering the necessary electrical current from the battery to the starter motor, enabling it to crank the engine.
- Reliability: High-quality battery cables are essential for a reliable and consistent startup. Faulty or corroded cables can lead to intermittent starts or complete failure.
- Safety: Defective battery cables can pose a fire hazard if they overheat or short circuit. Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial for safety.
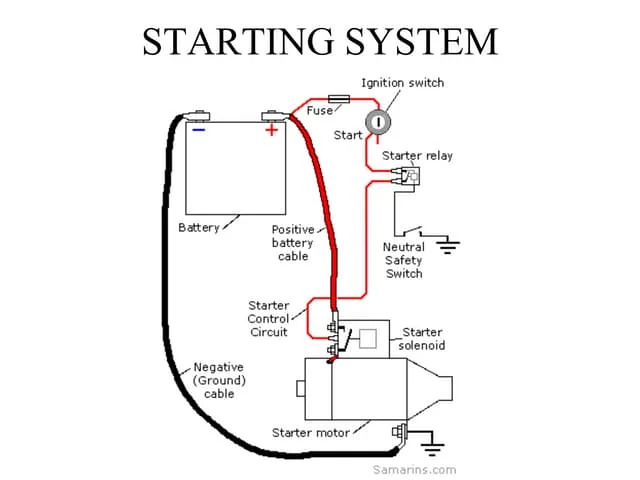
How the starting system works
1. Ignition: When you turn the ignition switch to the “start” position, it completes the electrical circuit between the battery and the starter relay.
2. Relay Activation: The starter relay, energized by the incoming current, closes its contacts, allowing high current to flow to the starter motor.
3. Starter Motor Engagement: The starter motor begins to rotate, turning the bendix drive, which engages with the flywheel.
4. Crankshaft Rotation: The starter motor’s rotation causes the flywheel to spin, turning the crankshaft and the engine’s pistons.
5. Combustion and Ignition: As the pistons compress the air-fuel mixture, a spark from the ignition system ignites it, creating a power stroke that helps the engine continue to rotate on its own.
6. Starter Motor Disengagement: Once the engine is running, the bendix drive disengages, preventing the starter motor from continuing to rotate.
Neutral safety switch
The primary function of the neutral safety switch is to prevent accidental engagement of the starter motor while the vehicle is in gear. This safety feature is essential to avoid sudden, uncontrolled movement that could lead to accidents, especially in congested areas or on inclines.When the gear selector is in a neutral position, the neutral safety switch is activated, allowing the starter motor to engage and crank the engine. However, if the gear selector is in any gear other than neutral, the switch is deactivated, preventing the starter motor from engaging.
Starting system problems
1. Weak Battery: A weak or dead battery is a common cause of starting problems.
2. Faulty Starter Motor: A damaged or worn starter motor can prevent the engine from cranking.
3. Ignition Switch Problems: A faulty ignition switch may not complete the electrical circuit properly.
4. Starter Relay Failure: A malfunctioning starter relay can prevent power from reaching the starter motor.
5. Bendix Drive Issues: Problems with the bendix drive can prevent the starter motor from engaging with the flywheel.
How is the starting system tested ?
Visual Inspection:
- Battery: Check for signs of corrosion, leaks, or physical damage.
- Cables: Ensure all cables are securely connected and free from corrosion.
- Starter Motor: Inspect for any visible damage or loose connections.
- Solenoid: Look for signs of overheating or damage.
- Ignition Switch: Check for loose or damaged components.
Electrical Testing:
- Battery Voltage: Use a voltmeter to measure the battery’s voltage. It should be around 12.6 volts when fully charged. If it’s significantly lower, the battery may need to be replaced.
Starter Motor Testing:
- Direct Testing: Remove the starter motor and connect it to a battery. If it rotates freely and powerfully, the starter motor is likely functioning correctly.
- Starter Tester: Use a starter tester to simulate engine load and test the starter motor’s performance.
Solenoid Testing
- Voltage Drop: Measure the voltage drop across the solenoid when the ignition key is turned. If the voltage drop is excessive, the solenoid may be faulty.
- Direct Bypass: Bypass the solenoid and connect the starter motor directly to the battery. If the starter motor works, the solenoid is likely the problem.
Ignition Switch Testing
- Voltage Measurement: Measure the voltage at the ignition switch terminals when the key is turned. If there’s no voltage, the ignition switch may be faulty.
- Direct Bypass: Bypass the ignition switch and connect the starter motor directly to the battery. If the starter motor works, the ignition switch is likely the problem.
Symptoms of a Bad Starter Motor
A well-functioning starter motor is essential for the reliable operation of your vehicle. If it fails, you’ll be unable to start your
engine. Common problems that can affect the starter motor include:
- Weak battery: A dead or weak battery can prevent the starter motor from receiving sufficient power.
- Faulty starter relay: The starter relay is a switch that controls the flow of electricity to the starter motor. If it’s damaged, the motor may not function properly.
- Worn brushes: Over time, the brushes in the starter motor can wear down, reducing their ability to conduct electricity.
- Bendix drive issues: The bendix drive can become damaged or worn, preventing the starter motor from engaging with the flywheel.
Starter motor repair options
Fortunately, there are several options available for repairing or replacing a malfunctioning starter motor:
1. DIY Repair
For those with mechanical aptitude and access to the necessary tools, attempting a DIY repair can be a cost-effective option. However, it requires a thorough understanding of the starter motor ‘s components and operation. Common DIY repairs include:
- Replacing brushes: Worn brushes can prevent proper electrical contact, leading to a faulty starter motor.
- Cleaning contacts: Corroded or dirty contacts can interfere with the starter motor’s electrical function.
- Tightening loose connections: Loose connections can cause intermittent starting problems.
2. Professional Mechanic
If you’re not comfortable tackling the repair yourself, a professional mechanic is the safest and often most efficient option. They have the expertise and tools to diagnose and repair various starter motor issues, including:
- Replacing the starter motor: In cases of severe damage or excessive wear, a complete replacement may be necessary.
- Overhauling the starter motor: For less severe damage, a mechanic can overhaul the starter motor by replacing worn or damaged components.
- Testing the electrical system: A faulty electrical system can also contribute to starter motor problems. A mechanic can test the battery, alternator, and related components.
3. Online Retailers and Auto Parts Stores
Many online retailers and auto parts stores offer a wide range of starter motors and replacement parts. You can purchase the necessary components and either install them yourself or have them installed by a mechanic. When shopping online, ensure you select a reputable seller and verify the compatibility of the parts with your vehicle.
Repair Cost of Starter Motor
1. DIY Repair: Could be as low as $50-$100 for parts, depending on the specific issue.
2. Professional Mechanic: Could range from $200-$500 or more, depending on the labor rates and the complexity of the repair.
3. Online Retailers and Auto Parts Stores: Similar to DIY repairs for parts, but you’ll still need to pay for labor if you have the parts installed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the starter motor is the catalyst that transforms a stationary machine into a moving force, a spark of energy that ignites the journey ahead.The starter motor, though often overlooked, plays a vital role in the operation of your vehicle. By understanding its mechanics, function, and common problems, you can take proactive steps to ensure its longevity and reliability. A well-maintained starter motor will keep your vehicle running smoothly and prevent unexpected breakdowns.