Introduction to ABS Sensor
ABS sensor, also known as a wheel speed sensor, is a critical component in modern vehicles that helps monitor wheel speed to prevent the wheels from locking up during braking. This sensor is integral to the ABS, which enhances vehicle control and safety,
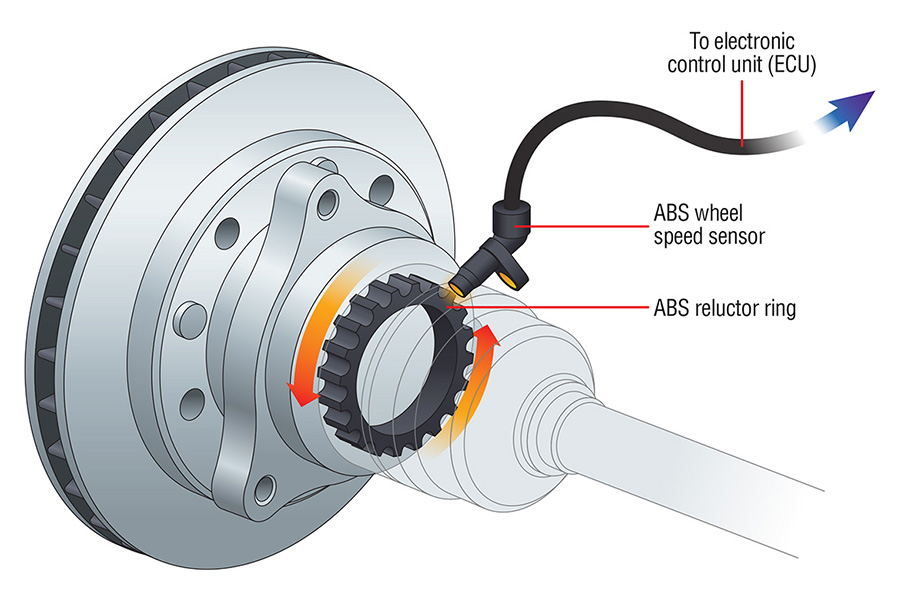
especially in adverse conditions such as wet or icy roads. ABS sensors detect changes in wheel speed and send signals to the ABS control module to modulate brake pressure, ensuring optimal braking performance.
Importance of ABS Sensor in Modern Vehicles
ABS sensor are vital for vehicle safety, as they prevent skidding and maintain traction during emergency braking situations. By providing real-time data to the ABS system, these sensors enable smoother stops and reduced stopping distances, significantly lowering the risk of accidents.
Brief History of ABS Systems
The concept of anti-lock braking dates back to aircraft in the 1950s. The technology was adapted for cars in the 1970s, initially featured in high-end luxury vehicles. As technology advanced, ABS became a standard safety feature in most vehicles, with sensors playing a pivotal role in its functionality.
How ABS Sensor Work
Basic Working Principle of ABS Sensor
ABS sensor operate by monitoring the rotational speed of each wheel. When a wheel is about to lock up during braking, the sensor detects a rapid deceleration and sends a signal to the ABS control module. The module then modulates the brake pressure to prevent the wheel from locking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control.
Key Components of an ABS Sensor
- Sensor Ring (Tone Ring): Often located on the wheel hub or axle, this ring generates a signal as it passes by the sensor.
- Sensor (Magnetic or Hall Effect): Positioned near the tone ring, it detects changes in the magnetic field caused by the ring’s movement.
- Wiring and Connectors: These components transmit the signal from the sensor to the ABS control module.
Types of ABS Sensor
There are two main types of ABS sensors: passive and active. Passive sensors generate their own voltage and require no external power, while active sensors need a power supply to operate and offer better performance in low-speed scenarios.
Types of ABS Sensor
Active vs. Passive ABS Sensors
- Active Sensors: More advanced and accurate, these sensors use a power supply and can detect wheel speed at very low speeds, even when the vehicle is nearly stationary.
- Passive Sensors: Older technology that operates without a power supply, passive sensors are generally less sensitive at low speeds.
Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are a specific type of ABS sensor that directly measure the speed of each wheel. They are critical for ensuring that the ABS can adjust braking pressure quickly and effectively during sudden stops.
Magnetic vs. Hall Effect Sensors
- Magnetic Sensors: Utilize a magnet and coil to generate a voltage as the sensor ring moves past, commonly found in older vehicles.
- Hall Effect Sensors: These are more modern and provide a digital signal, which is more precise and easier to interpret by the ABS control module.
Functions of ABS Sensor
Real-Time Monitoring of Wheel Speed
ABS sensor continuously monitor wheel speed and send data to the ABS control module. This real-time information is crucial for adjusting brake pressure during sudden stops or when traction is compromised.
Prevention of Wheel Locking
By detecting potential wheel lock-up, ABS sensor enable the ABS to modulate brake pressure. This prevents wheels from skidding and helps maintain steering control, especially during emergency braking.
Enhancing Vehicle Stability and Control
ABS sensor work in tandem with other stability control systems, such as Electronic Stability Control (ESC) and Traction Control System (TCS), to ensure the vehicle remains stable and manageable during complex driving conditions.
Key Components of ABS Systems
ABS Control Module
The ABS control module is the brain of the ABS system, interpreting signals from the sensors and adjusting brake pressure accordingly to prevent wheel lock-up.
ABS Pump
The ABS pump restores the pressure in the braking system after it has been modulated by the control module, ensuring
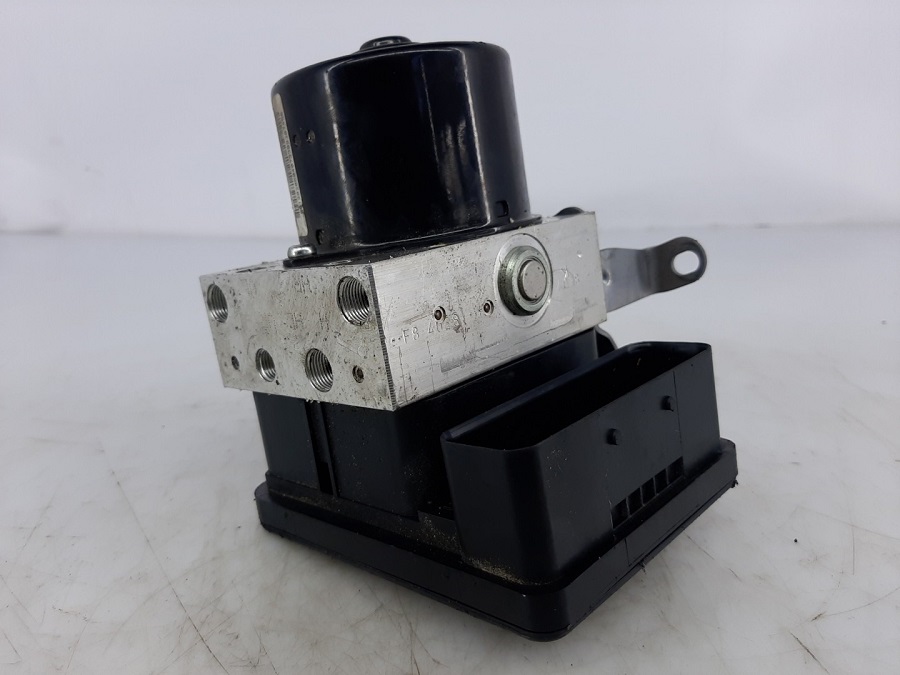

consistent braking performance.
Valves and Sensors
Valves control brake pressure at each wheel, while sensors provide the critical data needed for the ABS to function effectively. Together, they ensure smooth and controlled braking.
Common Symptoms of Faulty ABS Sensor
ABS Warning Light On
One of the most common signs of a malfunctioning ABS sensor is the illumination of the ABS warning light on the dashboard. This indicates that the system has detected an issue, often related to a sensor fault.
Inconsistent Braking
If you experience inconsistent braking, such as jerky stops or a pulsating brake pedal, it could be a sign of a faulty ABS sensor that’s not accurately detecting wheel speed.
Unusual Brake Pedal Behavior
A soft or unusually hard brake pedal can also signal ABS sensor issues, as the system may not be able to adjust brake pressure correctly.
Causes of ABS Sensor Failure
Physical Damage or Contamination
ABS sensors are located near the wheels and are prone to physical damage from road debris, dirt, and moisture. This contamination can interfere with sensor readings and lead to failure.
Electrical Issues
Wiring problems, such as corroded connectors or damaged cables, can disrupt the signal between the sensor and the ABS control module, causing errors in sensor functionality.
Wear and Tear Over Time
Like any other automotive component, ABS sensors can wear out over time due to exposure to harsh conditions and constant use, leading to degraded performance.
Diagnosing ABS Sensor Problems
Tools and Techniques for Diagnosing ABS Issues
Diagnosing ABS sensor issues typically involves visual inspection, signal testing, and using specialized diagnostic tools to read fault codes.
Using OBD-II Scanners
An OBD-II scanner can be used to check for fault codes related to ABS sensor problems. These codes provide insights into which sensor is malfunctioning and why.
Inspecting Sensor Wiring and Connectors
Inspecting the sensor’s wiring and connectors for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections can help identify the root cause of ABS sensor malfunctions.
Replacing ABS Sensor
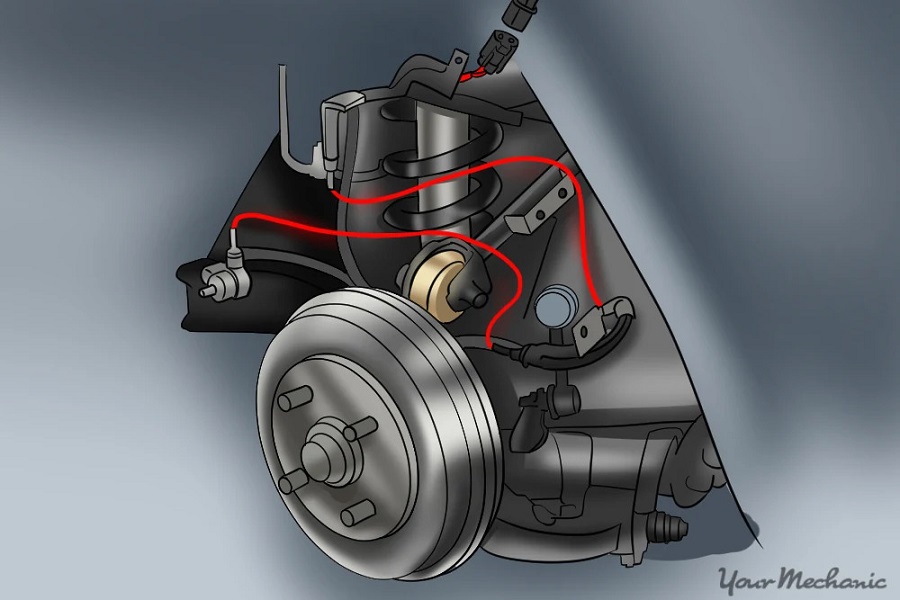
Step-by-Step Guide to ABS Sensor Replacement
- Locate the Faulty Sensor: Identify the sensor that needs replacement using diagnostic tools.
- Remove the Wheel: Access the sensor by removing the wheel and any necessary components.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Carefully disconnect the old sensor from its wiring.
- Install the New Sensor: Attach the new sensor and reconnect the wiring securely.
- Test the System: Once replaced, test the ABS system to ensure proper operation.
Tools Needed for Replacement
Basic tools required include a jack, lug wrench, socket set, and possibly a torque wrench, depending on the vehicle.
Safety Precautions
Always ensure the vehicle is securely lifted and supported when working on ABS sensors, and avoid touching the sensor with bare hands to prevent contamination.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Regular Inspection of ABS Sensor
Regularly inspect ABS sensors for signs of damage, dirt, or corrosion. Keeping sensors clean and free from contaminants helps maintain their accuracy.
Keeping Sensors Clean
Cleaning the sensor area with a gentle brush or cloth can prevent debris from interfering with the sensor’s operation.
Monitoring Electrical Connections
Regularly check sensor connections for corrosion or wear, ensuring reliable communication between the sensor and ABS control module.
Benefits of ABS Sensor
Improved Vehicle Safety
ABS sensor play a critical role in vehicle safety by ensuring the ABS functions correctly, helping prevent skidding and loss of control during braking.
Enhanced Braking Performance
By continuously monitoring wheel speed and adjusting brake pressure, ABS sensors help achieve optimal braking performance, reducing stopping distances.
Reduction in Accident Risk
The enhanced control provided by ABS sensors reduces the likelihood of accidents, particularly on slippery or uneven surfaces.
ABS Sensors in Modern Cars
Integration with Other Safety Systems
Modern vehicles integrate ABS sensor with other safety technologies like Electronic Stability Control (ESC) and Traction Control Systems (TCS) to provide comprehensive vehicle stability.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in ABS sensor technology, such as the use of Hall Effect sensors and digital signal processing, have improved sensor accuracy and response times.
Future Trends in ABS Technology
Future developments may include the integration of ABS sensors with autonomous driving technologies, further enhancing vehicle safety and control.
Cost of ABS Sensor Replacement
Factors Affecting the Cost
The cost of replacing an ABS sensor depends on the vehicle make and model, labor rates, and whether OEM or aftermarket parts are used.
DIY vs. Professional Replacement
While some may choose to replace ABS sensors themselves to save money, professional replacement ensures proper installation and system calibration.
Average Cost Estimates
On average, ABS sensor replacement costs range from $100 to $300 per sensor, including parts and labor.
Frequently Asked Questions
Common Questions About ABS Sensors
- What happens if my ABS sensor fails? If an ABS sensor fails, the ABS system may not function correctly, leading to reduced braking performance and increased risk of wheel lock-up.
- Can I drive with a faulty ABS sensor? Driving with a faulty ABS sensor is not recommended, as it compromises vehicle safety by disabling the ABS.
- How often should ABS sensors be replaced? ABS sensors typically last the lifetime of the vehicle but may need replacement if damaged or malfunctioning.
Troubleshooting ABS Sensor Issues
Regular diagnostic checks and inspections can help identify ABS sensor issues early, preventing more severe braking problems.
How to Extend the Life of ABS Sensor
Regular maintenance, such as keeping sensors clean and inspecting connections, can help extend the life of ABS sensors.
Conclusion
ABS sensor are crucial for vehicle safety, ensuring optimal braking performance and control during emergency stops. By monitoring wheel speed and preventing wheel lock-up, they enhance overall vehicle stability.