Introduction to Hybrid Vehicles
In the modern world, fuel efficiency, environmental awareness, and technological innovation have become central to how we think about transportation. One term that consistently pops up is hybrid vehicles. But how do hybrid vehicles work, and why have they become such a popular choice among drivers around the world? If you’ve ever wondered how a car can switch between gasoline and electricity so seamlessly, you’re not alone. Hybrid vehicles are designed to offer the best of both worlds—combining fuel savings with lower emissions, without sacrificing driving performance or convenience.
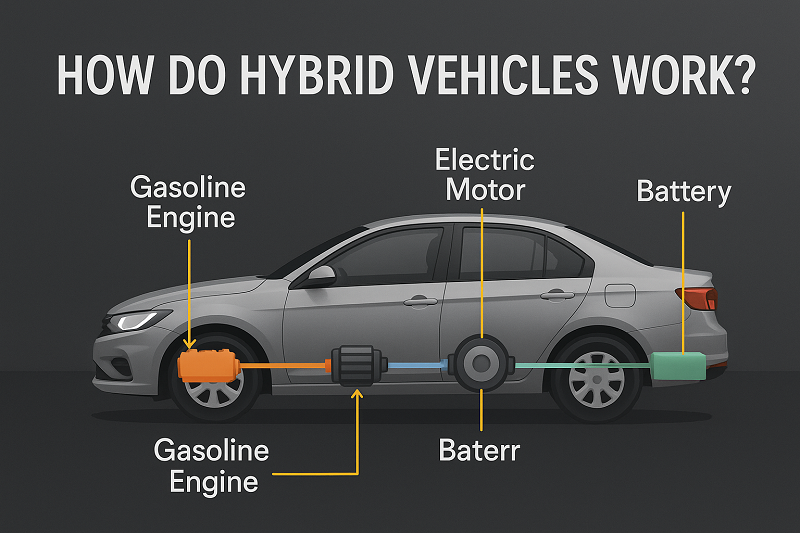
The name hybrid itself suggests a blend. In this case, it’s the blending of a traditional internal combustion engine with an electric motor. Unlike standard vehicles that rely solely on gasoline to move from point A to point B, hybrid cars smartly alternate between or combine the use of fuel and electric power to optimise efficiency. Whether you’re stuck in city traffic or cruising on the highway, hybrids adjust their power delivery to suit your needs, silently switching between systems through advanced technology that most drivers never even notice.
The Three Types of Hybrid Vehicles Explained
The inner workings of a hybrid car depend significantly on which type of system it uses. Today, there are three primary types of hybrid vehicles found on the market: parallel hybrids, series hybrids, and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs). Though they all aim to reduce fuel consumption and emissions, each type achieves this goal in a different way.
1. Parallel Hybrids
This is the most common form of hybrid, and it’s used in well-known models such as the Toyota Prius and the Honda Insight. In a parallel hybrid, both the gasoline engine and the electric motor are directly connected to the car’s transmission. This means they can either work together or independently to power the wheels. At lower speeds, the electric motor often does the heavy lifting, while the gasoline engine activates when additional power is needed—for example, during acceleration or uphill driving. This shared responsibility improves fuel economy and reduces strain on the engine.
2. Series Hybrids
Series hybrids operate differently. Vehicles like the BMW i3 with range extender use a gasoline engine solely to generate electricity. That power either recharges the battery or is sent directly to the electric motor, which is the only component that drives the wheels. As a result, the driving experience is very similar to that of a fully electric car—quiet, smooth, and responsive—especially during city driving where constant acceleration and braking are common.
3. Plug-In Hybrids (PHEVs)
PHEVs push the hybrid concept even further. These vehicles have a much larger battery pack that can be charged using an external power source, just like an electric vehicle. Cars such as the Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV or the Toyota RAV4 Prime can drive for longer distances solely on electricity. For drivers with short commutes, this often means they can use electric power for daily travel and rarely rely on gasoline, making them ideal for those who want to reduce fuel use without sacrificing flexibility.
Hybrid Battery System and Regenerative Braking
One of the standout features of hybrid vehicles is their advanced battery system. Unlike traditional cars that use a simple 12-volt battery to start the engine and run accessories, hybrid vehicles are equipped with high-voltage battery packs, usually made from lithium-ion or nickel-metal hydride. These batteries power the electric motor and are constantly being recharged through a brilliant process known as regenerative braking.
Regenerative braking is where hybrid technology shines. In a regular vehicle, the energy produced when you brake is wasted as heat. However, in a hybrid, this energy is not wasted—it’s converted back into electrical energy and stored in the battery. This contributes significantly to the car’s overall efficiency and allows it to use less fuel over time.
Here’s how regenerative braking compares to traditional braking:
| Feature | Traditional Cars | Hybrid Vehicles (Regenerative Braking) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy during braking | Lost as heat | Recovered and stored as electricity |
| Impact on fuel efficiency | No fuel savings | Improves fuel economy |
| Battery involvement | Minimal (12V only) | High-voltage system recharged while driving |
Seamless Power Transition and Smart Fuel Use
One of the most fascinating aspects of hybrid vehicles is how seamlessly they switch between power sources. Advanced onboard computer systems are constantly monitoring your driving conditions—such as speed, throttle input, battery charge, and terrain—and deciding whether to use electricity, gasoline, or both. This smooth switching process happens without any noticeable lag, making hybrids feel incredibly refined during operation.
Whether you’re in slow-moving traffic or accelerating onto a highway, hybrids make smart choices in real time. That’s why many drivers report that hybrids feel unusually quiet and efficient without requiring them to think about what’s powering their ride at any given moment. This efficiency doesn’t just feel good—it results in real savings and environmental benefits.
Fuel Economy and Environmental Benefits of Hybrids
The primary reason people turn to hybrid vehicles is simple: better fuel efficiency. By reducing reliance on gasoline and making use of electric power when it makes the most sense, hybrids significantly reduce the number of fuel stops a driver needs to make. Over time, this can lead to hundreds—or even thousands—of dollars saved at the gas pump.
But it’s not just about personal savings. Hybrid vehicles emit fewer greenhouse gases than traditional gasoline cars. While they still use fuel, they do so more effectively and responsibly. This makes hybrids a practical middle ground between conventional gas vehicles and full electric models, especially for those who aren’t ready to commit entirely to battery-electric driving.
Let’s compare fuel usage between different vehicle types:
| Vehicle Type | Fuel Dependency | Emissions | Typical Range (Electric Only) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gasoline Vehicle | 100% gasoline | High | None |
| Hybrid Vehicle | Gasoline + Electric | Moderate | Limited (low-speed only) |
| Plug-In Hybrid | Primarily Electric | Low | 20–50 miles (depends on model) |
| Electric Vehicle | 100% Electric | Zero tailpipe | 150–400 miles |
Cost, Maintenance, and Long-Term Value
One common concern with hybrids is the initial cost. Due to their complex systems and high-voltage batteries, hybrid vehicles are often priced higher than comparable gasoline-only models. However, this cost difference can be offset over time through fuel savings, lower emissions, and government incentives, such as rebates and tax credits.
Hybrids also tend to experience lower maintenance costs. Because the electric motor often assists or replaces the gasoline engine, there is less wear and tear on mechanical parts like the transmission or brake pads. This leads to longer component lifespans and fewer costly repairs in the long run. For drivers who prioritise both reliability and lower total ownership costs, hybrids are often a smarter long-term choice.
Performance, Misconceptions, and Future of Hybrid Technology
A common myth about hybrid cars is that they are slow or underpowered. This couldn’t be further from the truth. The instant torque provided by electric motors often makes hybrid vehicles quicker off the line than some traditional cars. High-performance hybrid models like the McLaren P1 demonstrate that hybrids can deliver breathtaking acceleration while still being efficient.
As battery and electric motor technologies continue to evolve, the future of hybrids looks brighter than ever. Innovations such as solid-state batteries promise lighter, more powerful, and longer-lasting energy storage. Meanwhile, automakers are expanding hybrid systems into larger vehicles like buses, trucks, and boats, broadening the environmental benefits of this smart technology across various industries.
Conclusion: Why Hybrids Are a Smart Automotive Solution
So, how do hybrid vehicles work? At their core, hybrids combine an electric motor and a gasoline engine in a system that adjusts intelligently to provide the most efficient, smooth, and responsible driving experience possible. With technology that reuses braking energy, switches power sources silently, and reduces emissions without compromising convenience, hybrids truly represent a meaningful step toward more sustainable transportation.
Whether you’re concerned about saving money, reducing your carbon footprint, or simply driving a technologically advanced vehicle, hybrid cars offer an elegant and accessible solution. In the ever-evolving world of transportation, hybrids stand as a symbol of balance, proving that smart innovation can improve both our driving and our environment.


